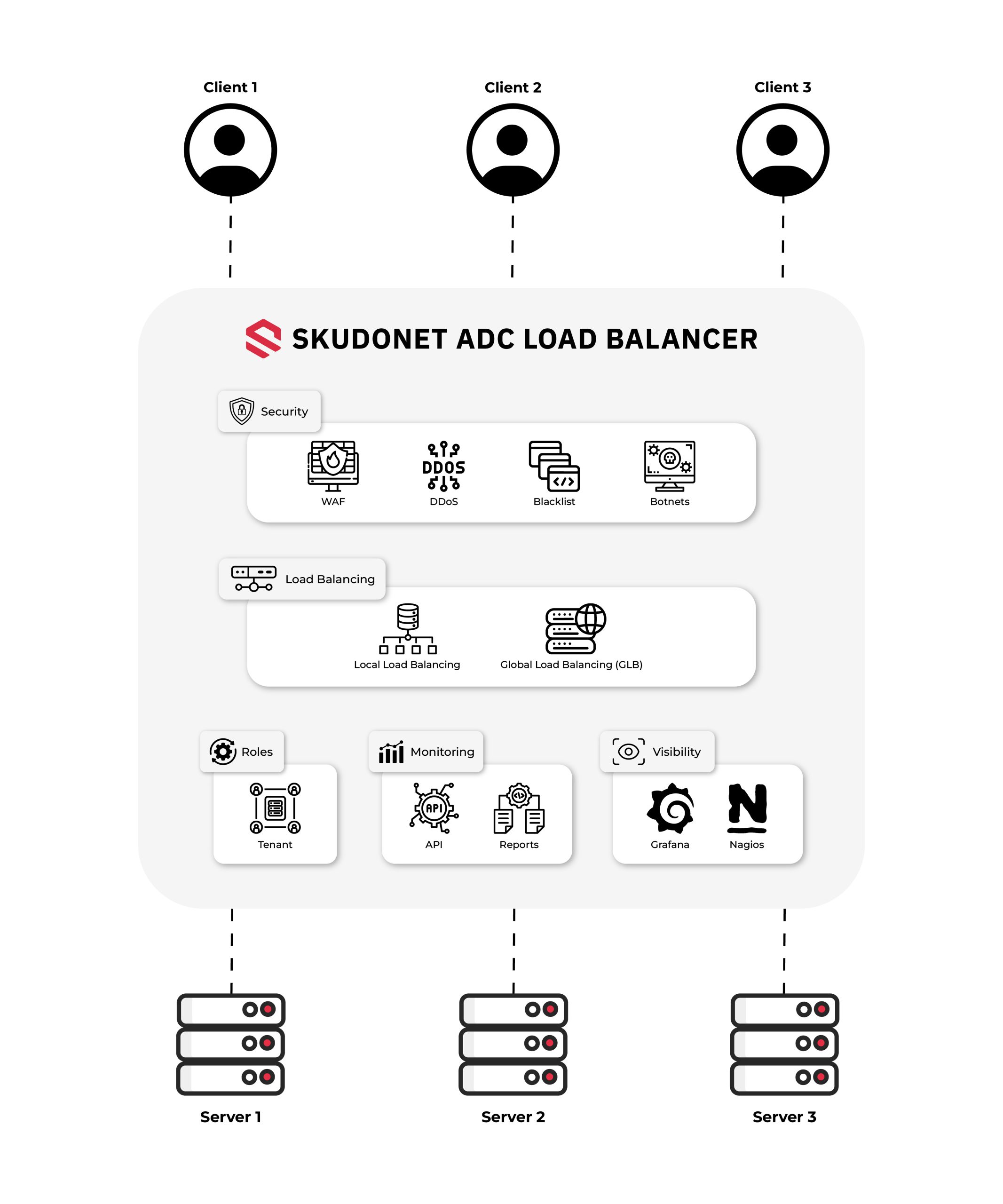
Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) are vital in the infrastructure of any organization that relies on online services. They manage the flow of data efficiently, ensuring that applications respond optimally. Unlike traditional load balancers, ADCs integrate security and optimization functions that enhance the user experience. In this article, we will explore how the ADC Load Balancer has become a key technology for advanced traffic management in networks.
The Role of ADCs in Load Balancing
Unlike traditional load balancers, which simply distribute network traffic among servers, ADC Load Balancers add a layer of intelligence to this process. By including features like application acceleration, session management, and security inspection, ADCs make complex decisions based on various parameters. This ensures that applications receive the appropriate traffic depending on their needs, enhancing both performance and reliability.
For example, while a traditional hardware load balancer might evenly distribute requests, an ADC can analyze which server is best suited to handle a specific request based on content or current load, optimizing the delivery of critical services.
Types of Load Balancers and Their Differences
It’s important to understand how ADCs relate to other types of load balancers, such as hardware load balancers and virtual IP load balancers.
- Hardware Load Balancer: Physical solutions placed within the network infrastructure to manage large volumes of traffic. These devices are essential for environments requiring high performance and low latency, such as data centers handling real-time transactions or large volumes of requests.
- Virtual Load Balancer: Software-based solutions that assign a virtual IP address to distribute traffic. This option is ideal for flexible infrastructures or virtualized environments where scalability and efficient resource use are critical. Explore the benefits of load balancing in multi-tenancy environments in our post Understanding Multi-Tenancy Load Balancer.
ADC Load Balancers not only distribute traffic like these solutions but also offer additional layers of control and analysis, from packet inspection to policy-based optimization.
Use Cases for ADC Load Balancers
ADCs have proven invaluable in multiple industries. Here are some common scenarios where ADC Load Balancers make a significant impact:
-
- E-commerce: For large e-commerce websites, ADC Load Balancers distribute traffic among servers to ensure that users experience fast load times, regardless of the number of simultaneous visits.
- Banking and Finance: Financial institutions require high levels of security and constant availability. ADCs help manage encrypted traffic and distribute loads among servers, ensuring efficient online service delivery.
- High Availability and Redundancy:SKUDONET’s ADC solutions ensure that if a server fails, requests are automatically rerouted to another available server, guaranteeing service continuity. This feature allows businesses to maintain a seamless user experience, even in the face of technical issues.
ADC Load Balancers are more than just traffic distribution tools; they are essential for the efficient and secure delivery of applications in complex environments. By adopting a solution like SKUDONET’s ADC, businesses can enhance both the user experience and the security of their systems. Whether you’re evaluating a hardware load balancer or a virtual load balancer, SKUDONET ADC provides that extra layer of control and optimization necessary for today’s business environments.
Discover how SKUDONET’s enterprise solutions can transform your application delivery strategy.