Contents
The SKUDONET Command Line Interface (skd-cli) is an essential tool for managing and automating load balancing tasks through a streamlined CLI experience. By integrating seamlessly with SKUDONET’s API, skd-cli provides advanced functionalities for both Community and Enterprise editions, making it a powerful solution for efficient infrastructure management.
What is SKUDONET’s Command Line Interface (CLI)?
skd-cli is the acronym of SKUDONET Command Line Interface. This tool allows managing multiple load balancers from a command line or through automation of open-source load balancer actions in operation scripts.
skd-cli is a wrapper for the SKUDONET API (Application Programming Interface). It features an autocompletion functionality to simplify navigation through load balancer modules and their objects.
It is compatible with SKUDONET Enterprise load balancers from version EE 6.3 and above and SKUDONET Community load balancer version 7.2 and above.
Step-by-Step Installation of Command Line Interface (skd-cli)
Installation
skd-cli is available in the official SKUDONET APT repositories and it can be installed in a SKUDONET load balancer using:
apt-get update && apt-get install skd-cli
This package is also compatible with Debian, Ubuntu, or any Debian-based distribution to execute commands remotely on SKUDONET load balancers.
Profiles
SKUDONET command line (skd-cli) contains information in regards to the load balancer where the commands will be executed and the user who will execute the command (root by default in Community Edition, root and RBAC users in Enterprise Edition). skd-cli can manage different profiles, each profile is a defined Load Balancer connection saving the following data.
Load balancer api key:
If the command skd-cli is executed out of a SKUDONET load balancer the system will require the remote Host and Port for connecting to the SKUDONET API, the IP and PORT for the API are the same as the one used for the web GUI.
The information of the configured profiles is saved in the user home, for root /root/.skd-cli .
Setup
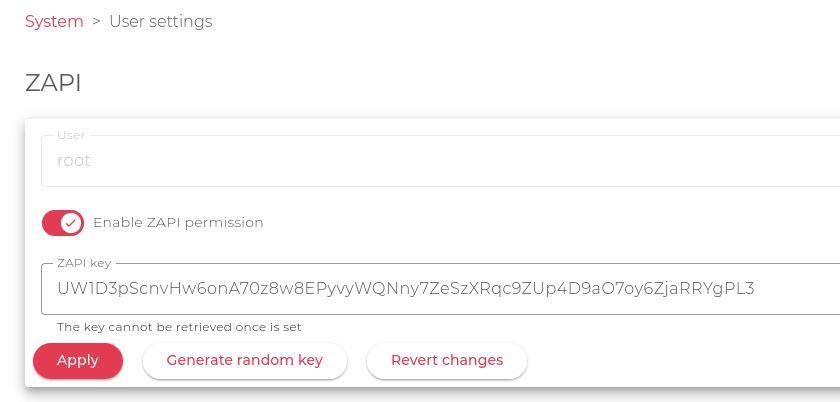
Before running skd-cli a ZAPI key is required. It can be enabled from the SKUDONET Web GUI, in the menu System > User settings.
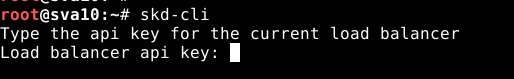
Once skd-cli is installed, it can be started by executing skd-cli in the shell. If it is executed from the load balancer, it will run with the default profile localhost which manages the local load balancer and the ZAPI key will be requested. In any other case, the configuration assistant will be started.
Once the API KEY is entered the system will run the first connection against the API and the prompt will be marked as OK (red and grey) in case the connection can’t be done, the prompt will be marked in grey.
![]()
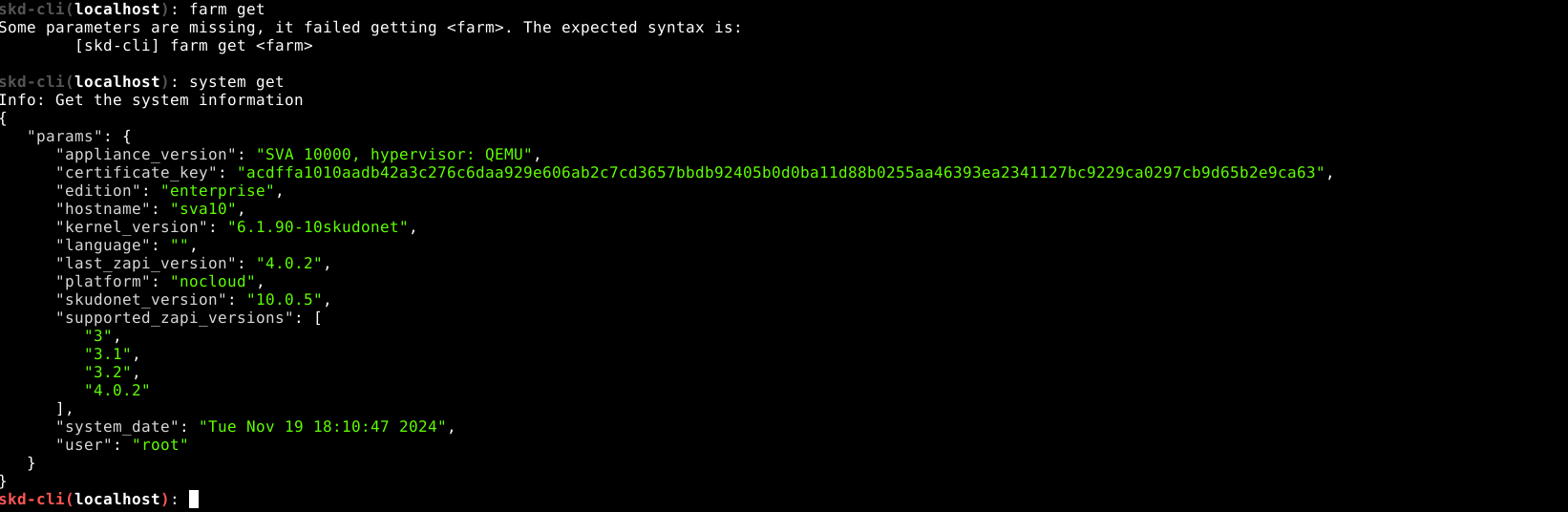
In case the connection against the API is OK, then the prompt will be shown as follows:
![]()
check the connectivity with some simple command, i.e. “system get” gives the default system information.
If the profile settings need to be modified or another profile needs to be created, skd-cli profile command should be executed.
It is possible to load an already configured profile during the skd-cli invocation time, using the -p option as shown below.
sh:~$ skd-cli -p my_profile
or using the command with skd-cli in an interactive mode:
skd-cli: profile apply my_profile
An example is shown below:
How it is used
skd-cli has two working modes:
1. Launched without arguments, the skd-cli shell is executed in interactive mode. This mode provides autocompletion and it does not finish once a command is executed, to exit from the skd-cli shell, type quit or press Ctrl+C. The default profile is loaded and it can be changed in any moment.
2. skd-cli is invoked with arguments. This will execute the command, without entering into the skd-cli interactive shell, and then return to the system console, the default localhost host profile is used, if you want to connect against another load balancer using a different profile please use -p <profile_name> paramenter.
Let’s see below the commands available in the SKUDONET Command Line Interface.
Commands and Parameters
A command has the following syntax:
sh:~$ skd-cli [ options ] [ object ] [action] [ ids list ] [ parameters ]
As an example:
sh:~$ skd-cli -nc -p test-lb2 farms-services-backend set farm1 service1 0 -ip 1.1.1.1 -port 80
Find below the description of every parameter.
options (-nc -p test-lb2): They are set in the skd-cli invocation. The complete option list is detailed in the help. No color (-nc) and load the profile test-lb2 (-p).
object (farms-services-backend): It is the kind of load balancer object that is selected, each object has a unique name, in this example, the command refers to the object backend inside a service of a farm.
action (set): It is the verb that will be executed.
ids list (farm1 service1 0): They are the identifiers that refer to the object. farm id: farm1, service id: service, backend id: 0.
parameters (-ip 1.1.1.1 -port 80): They are the parameters to set in the object. Mostly, they are expected when an object is created/added or modified.
All these parameters can be used in JSON format using the -j (–json) option.
The expected command arguments can be retrieved by pressing Enter. Sometimes parameters are not expanded until the previous arguments are set.

skd-cli includes an auto-completion functionality that can be triggered by pressing the double TAB button.
The updated help can be checked with the command below.
skd-cli help
Output Data
The output is printed in a coloured JSON format, but they can be disabled by invoking skd-cli with the option -nc (–no-colors). Some information messages could be shown, those messages are omitted when skd-cli is launched in command execution mode (without interactive skd-cli).
The error messages are displayed through the STDERR output.
Command Examples
A complete list of examples can be queried in the API documentation. Here are only some useful examples:
Get system info
sh:~$ skd-cli system get
Get system stats
sh:~$ skd-cli statistic-system get
List an overview of the farms
sh:~$ skd-cli farm list
Create a farm
sh:~$ skd-cli farm create -profile http -farmname farm1 -vip 10.0.0.241 -vport 443
Retrieve the configuration of a farm
sh:~$ skd-cli farm get farm1
Modify a farm
sh:~$ skd-cli farm set farm1 -listener https
Restart a farm
sh:~$ skd-cli farm restart farm1
Create a service
sh:~$ skd-cli farm-service add farm1 -id images
Modify a service
sh:~$ skd-cli farm-service set farm1 images -urlp /images
Add a backend
sh:~$ skd-cli farm-service-backend add farm1 images -ip 10.0.4.40 -port 443
Modify a backend
sh:~$ skd-cli farm-service-backend set farm1 images 0 -priority 1
Delete a backend
sh:~$ zcli farm-service-backend remove farm1 images 0
Unset a backend in maintenance mode
sh:~$ skd-cli farm-service-backend maintenance farm1 images 0
Set a backend in maintenance mode
sh:~$ skd-cli farm-service-backend non_maintenance farm1 images 0
Source Code Repository
The skd-cli source code project is available in the URL https://github.com/Skudonet/zcli take into consideration that any reference to zcli is compatible with skd-cli, zcli command is the previous project name integrated with ZEVENET versions.
Enjoy skd-cli, the SKUDONET Command Line Interface!