Edge Computing & the Future of Load Balancers
Edge computing is revolutionizing the way data is handled, bringing processing closer to the source of data generation. The cloud edge is where this revolution truly takes shape, offering edge use cases that were previously impractical. Unlike traditional centralized computing, which relies on distant data centers, edge computing brings processing power directly to the devices and locations where data is generated. This shift from the cloud to the edge is driven by various factors, including the need for more reliable and real-time processing, the edge security, and privacy and security concerns.
SKUDONET ADC facilitates load balancing in edge environments, integrating seamlessly in Azure, AWS, Google Cloud, and SKUDONET Cloud Service for efficient edge computing solutions.
Contents
- 1 Edge Computing & the Future of Load Balancers
- 2 Understanding Edge Computing and Load Balancers
- 3 Benefits of Edge Computing in Load Balancing
- 4 Challenges and Disadvantages of Load Balancers in Edge Computing
- 5 SKUDONET ADC: Load Balancer in Edge Computing
- 6 How SKUDONET is used in the Edge
- 7 Future Trends in Load Balancers
Understanding Edge Computing and Load Balancers
Introduction to Edge Computing
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data near the edge, where it is generated, rather than relying on a centralized data center. Use cases that drive edge computing extend far beyond just faster, more reliable processing. Edge computing enables real-time applications, supports IoT and edge devices, and facilitates content delivery networks that reduce latency for users.
The Importance of Load Balancers in Edge Computing
Load balancers play a crucial role in edge computing, ensuring that traffic is distributed efficiently across the network edge. By distributing workload across multiple servers or resources, load balancers help optimize performance and ensure faster, more reliable service for users. In edge computing, load balancers are optimized for the location where data is generated, allowing for more quickly and efficiently managed traffic.
44% of organizations are investing in edge IT to create new customer experiences and improve engagement.
IDC Edge View 2023
Benefits of Edge Computing in Load Balancing
Edge computing offers several benefits for load balancing. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing reduces latency and improves real-time responsiveness for users. Additionally, edge computing can help offload processing tasks from centralized data centers, reducing the need for expensive infrastructure and improving scalability.
- Edge computing brings several benefits when it comes to load balancing, enhancing the overall performance and efficiency of data processing. Below are some key advantages:
- Reduced Latency Optimization
- Improved Scalability
- Proximity-Based Routing
- Security
- Cost Savings
- Sovereignty
Increases Speed: Reduced Latency Optimization
Reduced latency is a crucial aspect of edge computing, allowing for faster data processing and response times. By optimizing latency, organizations can ensure real-time interactions and quick decision-making processes.
Improved Scalability
Scalability is essential in the dynamic digital landscape, and edge computing offers enhanced scalability options for load balancing. It allows organizations to easily adjust resources based on demand, ensuring smooth operations even during peak usage.
Proximity-Based Routing
Proximity-based routing in edge computing enables data to be directed to the geographically closest edge server, reducing latency and improving overall network performance. This approach ensures efficient data transfer and enhances user experience.
Security
Security is also an advantage of edge computing, as it enables better compliance with GDPR requirements by storing data as close to the user as possible.
Cost savings
Edge computing limits costs by using a distributed infrastructure that allows for maximum optimisation of resources.
Sovereignty
Edge computing allows data to be processed as close to the user as possible, avoiding the need to send data over long distances to centralised data centres. In a context where privacy and data protection regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, edge computing offers a solution to meet GDPR requirements in certain countries by storing data as close to the user as possible and alleviating fears related to data sovereignty.
Challenges and Disadvantages of Load Balancers in Edge Computing
While edge computing offers many advantages, it also presents challenges for load balancing. Managing distributed resources and ensuring consistent performance across the network can be complex. Additionally, edge computing environments may have limited storage and processing resources compared to centralized data centers, requiring careful resource allocation and management.
At SKUDONET we are aware of the following issues and we have been ahead of our competitors in solving these problems.
Complexity in Implementation
Implementing load balancers in edge computing environments can be complex. The distributed nature of edge computing requires a meticulous setup to ensure seamless operation. Configuring load balancers to effectively distribute traffic while maintaining high availability and performance can be challenging. Additionally, the integration of load balancers with existing infrastructure poses integration complexities.
SKUDONET is easy to manage, both edge and on-premise.
Maintenance
While maintenance is crucial to the performance of this technology, with SKUDONET it is easy to manage, thanks to a system of subscriptions and updates.
Security Concerns
Security is a paramount concern in edge computing when it comes to load balancers. With data being processed closer to the source, the exposure to vulnerabilities increases. Malicious attacks can target the distributed nature of edge computing, potentially compromising sensitive information. Secure encryption protocols must be implemented to safeguard data in transit and at rest.
SKUDONET has an intrusion prevention and detection system (IPDS). Protection is carried out in different ways, the content of the web request is analysed using WAF, botnets are blocked or even filters are applied to protect against denial of service attacks. All this process of analysis and security is taken to the Edge in such a way that the clean, secure data is delivered to the client’s facilities, carrying out all the processing in the cloud and having the capacity to scale the Edge in resources (CPU/traffic/MEMORY/protection rules, etc.) on demand.
Dependency on Network Infrastructures
Edge computing heavily relies on network infrastructures, and load balancers are no exception. The effectiveness of load balancers in edge environments is heavily dependent on robust network connections. Issues such as network latency, bandwidth limitations, and network congestion can impact the overall performance of load balancers.
SKUDONET ensures reliable network connectivity which is essential for optimal load balancing functionality.
Ready to test SKUDONET ADC?
Discover the complete range of SKUDONET Load Balancing Products or request your free 30-day fully functional trial version of our SKUDONET ADC.
SKUDONET ADC: Load Balancer in Edge Computing
SKUDONET offers advanced application delivery controllers (ADCs) that can be used for edge computing environments. Our load balancers are optimized for the edge, providing real-time traffic management and ensuring high availability and performance for edge computing applications.
Deployment in the Edge Environment
Deploying SKUDONET ADC in the edge environment ensures streamlined data processing and distribution. This deployment strategy enhances the overall performance of edge devices by ensuring seamless communication and data management.
Integration in the Customer’s DMZ
Integrating SKUDONET ADC in the customer’s DMZ ensures enhanced security and streamlined data flow. It acts as a centralized hub for managing incoming and outgoing data and optimizing network performance and security measures.
Seamless Implementation in Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud
SKUDONET ADC seamlessly integrates with leading cloud providers like Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud. This integration allows for efficient load balancing across multi-cloud environments, ensuring optimal performance and scalability.
SKUDONET Cloud Service
SKUDONET Cloud Service offers a comprehensive cloud-based solution for implementing SKUDONET ADC. This service provides advanced load balancing capabilities in the cloud, allowing for efficient data processing and distribution across different cloud platforms.
How SKUDONET is used in the Edge
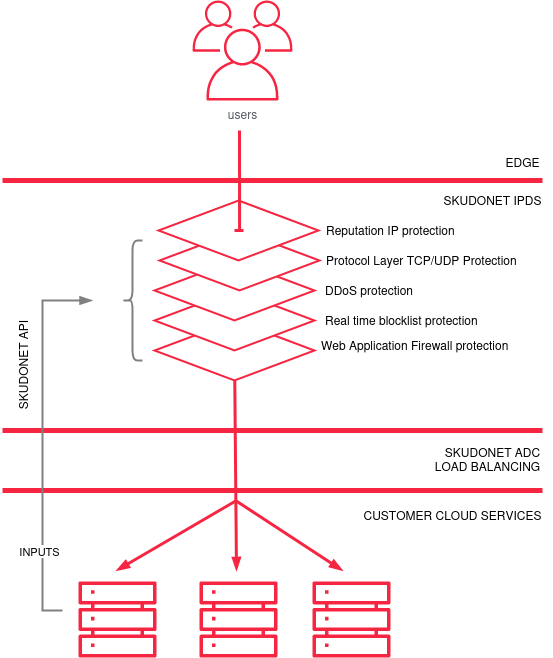
SKUDONET ADCs are deployed at the edge, where they efficiently distribute traffic across edge computing resources. By providing real-time traffic management and optimization, SKUDONET ADCs ensure that edge computing applications perform reliably and efficiently.
If you want to go deeper into how SKUDONET ADC works in the cloud, take a look at our Knowledge Base article.
SKUDONET Multi-Layered Security Overview in the Edge
Future Trends in Load Balancers
As edge computing continues to evolve, load balancers will play an increasingly important role. Future trends include the integration of edge computing capabilities directly into load balancers, enabling even more efficient and real-time traffic management. Additionally, advancements in hardware, software, and edge computing technologies will further enhance the performance and scalability of edge computing environments.
Adoption of Dynamic Load Balancing
The adoption of dynamic load balancing is essential for optimizing network performance in edge computing environments. By dynamically distributing network traffic based on real-time conditions, dynamic load balancers can ensure efficient utilization of resources and improved user experience.
Real-Time Monitoring Capabilities
Real-time monitoring capabilities play a crucial role in edge computing, providing insights into network performance and resource utilization. With real-time monitoring tools, organizations can quickly identify and address issues, leading to enhanced network reliability and performance.
Implementation of Adaptive Algorithms
The implementation of adaptive algorithms enables load balancers to dynamically adjust to changing network conditions. By leveraging machine learning and AI technologies, load balancers can optimize routing decisions, enhance resource allocation, and improve overall network efficiency.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Performance optimization techniques are essential for maximizing the efficiency and scalability of edge computing systems. By implementing performance optimization strategies such as caching, compression, and content delivery networks, organizations can achieve faster response times, reduced latency, and improved overall system performance.
We hope this article has answered your questions on this topic and has been of interest to you. If so, we would be grateful if it could be shared.
See you in the next article!