Local Service Load Balancing (LSLB)
The LSLB module balances traffic across pools of servers located within a data center. It supports a variety of protocols, including HTTP, TCP, UDP, SCTP, SIP, FTP, TFTP, PPTP, and SNMP. The LSLB module improves traffic performance, reliability, and scalability.
Actions
Use the following buttons to create and manage your farms:
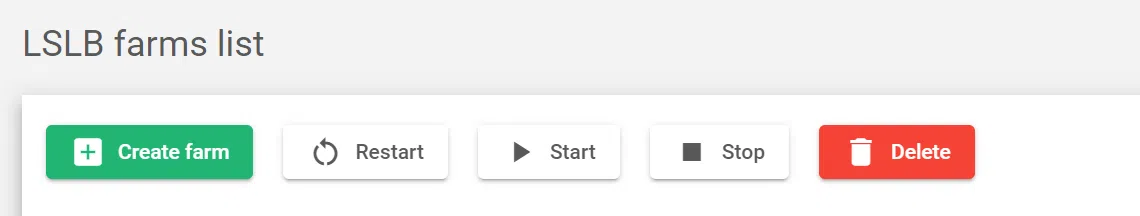
- Create Farm: Create a new farm that balances traffic across a pool of servers. You can choose from three different profiles: HTTP, HTTPS, and L4xNAT.
- Restart: Restart the selected farm. This can be useful if the farm is experiencing problems.
- Start: Start the selected farm. This will allow the farm to start balancing traffic again.
- Stop: Stop the selected farm. This will prevent the farm from balancing traffic.
- Delete: Delete the selected farm. This will remove the farm from the system and all of its configuration data.
Important Notice!
To select multiple farms, check the boxes next to their names.
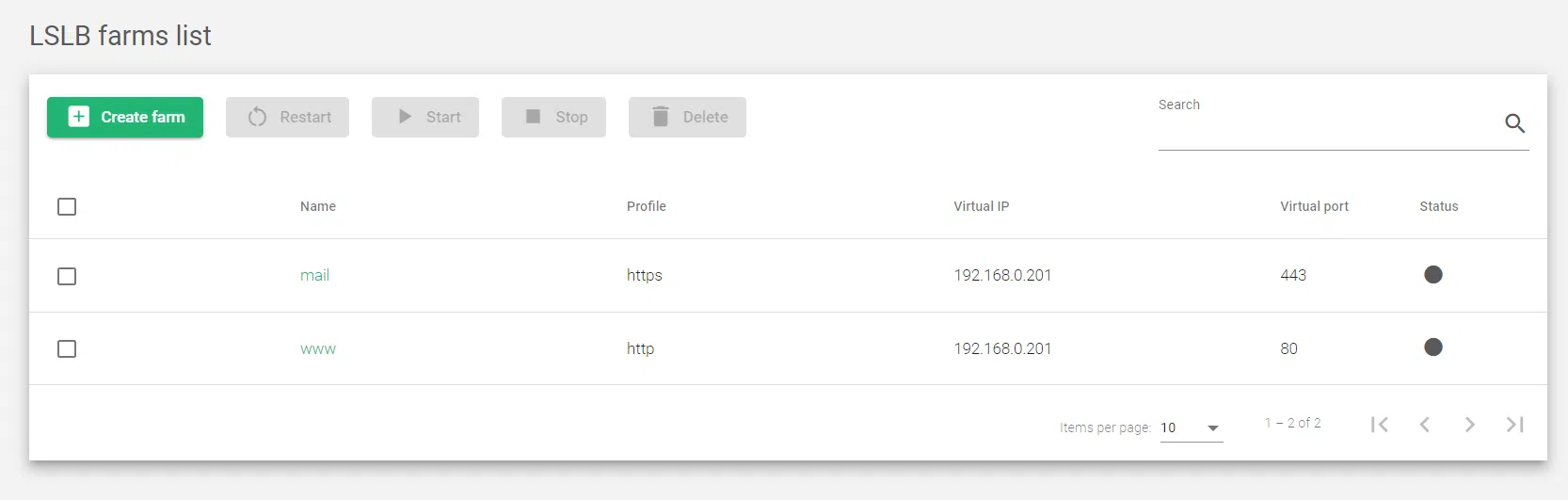
Content Table
This table contains farm listings and their properties.
This section describes the information that is displayed for each farm.
Name: A unique identifier for the farm, such as www or mail.
Profile: The type of traffic that the farm handles, such as HTTP, HTTPS, or L4xNAT.
Virtual IP: The IP address that clients use to access the farm.
Virtual Port: The port number that clients use to access the farm.
Status: The current state of the farm, such as Running, Stopped, or Restarting. These are the status indicators:
- Green: The farm is running and all nodes are available.
- Red: The farm has stopped.
- Yellow: The farm needs to be restarted for recent updates to take effect.
- Black: The farm is running but all nodes are unavailable or in maintenance mode.
- Blue: The farm is running but at least one node is unavailable.
- Orange: The farm is running but at least one node is in maintenance mode.
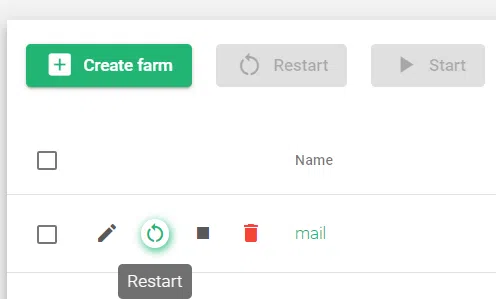
Actions: Each farm can be managed by clicking the icons in the image below.
- Edit: Modify the farm’s configuration. You can only change the farm’s name when the farm is stopped.
- Restart: Reboot the farm.
- Stop: Deactivate the farm and release the port it is using.
- Start: Activate the farm if inactive.
- Delete: Permanently delete the farm and all of its configuration files. The IP address and port will be released.
Next Article: Creating an LSLB Farm