SKUDONET Load Balancer is designed to be integrated into as many subnets as possible. The system has been designed with a routing system based on rules and routing tables. A rule is a condition that the packet has to match, and a routing table is where the packet is sent if the rule matches.
Tables can be modified but not created in SKUDONET v10, and each network interface has its routing table. You can modify the default behaviour of each routing table by adding/deleting/modifying the rules inside the table, this view lets the system administrator modify the default behaviour of the table.
Update a certain Routing table
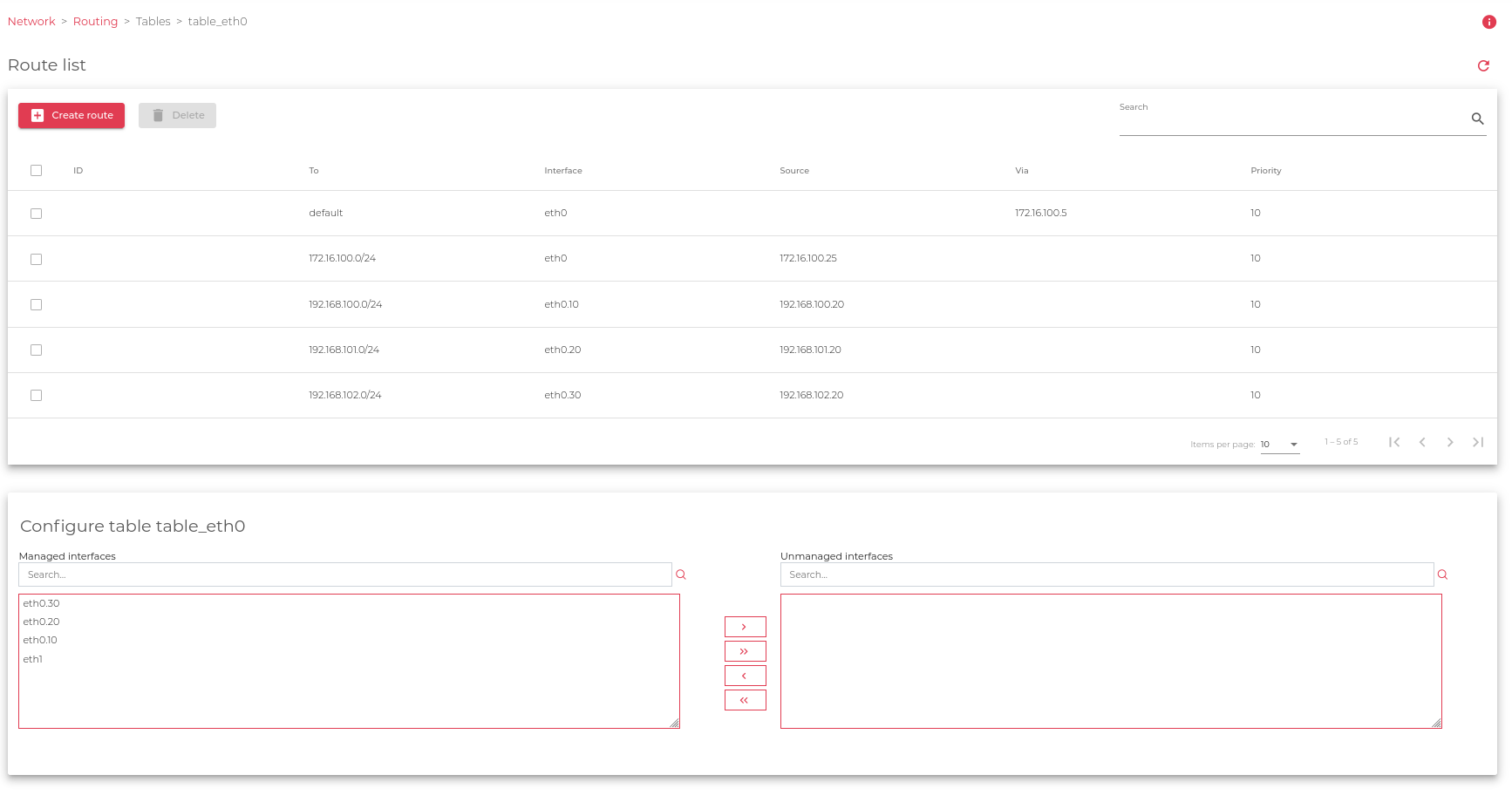
The global view for the routing table shows the following information.
This table shows the rules already configured in the system. The fields are described below:
ID. A unique internal identifier is assigned to the route. This value can’t be configured or modified. The default routes preloaded by the system can’t be deleted or modified.
To. Destination. This rule will be used in the case the destination matches.
Interface. Used interface to reach the destination configured previously in the field To.
Source. Source IP configured in the network communication, this IP will be used as the source IP in the connection, it also can be used as a source NAT configuration.
Via. The next hop where to send the package in case the destination is not accessible directly, it is used as a gateway to reach the data configured in field To.
Priority. Used to gauge which route has higher authority over the others. This property can be altered. But by default, the system assigns a number with a higher priority. i.e. The less the number, the higher the priority.
Bulk actions:
Delete. To remove a rule from the rules table.
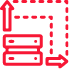
Managed and Unmanaged interfaces
Each routing table can use any local network interface to reach a certain destination, in case you need to misconfigure a certain Network interface of a certain routing table please move the network card to the Unmanaged Interface section.
A real example of usage:
eth0 is used for reaching backends and eth1 for management purposes, both Cards eth0 and eth1 are configured in the SKUDONET Appliance, but there is a Virtual IP configured upon the eth0 NIC card, the backend configured is in the Management network, as SKUDONET Default behaviour, this particular backend configured in the management network will be directly accessible using the eth1, but if eth1 is moved to “Unmanaged section” the load balancer will forward the request to the default Gateway in eth0 instead of accessing directly.