Contents
Updating GSLB Farms
Updating your GSLB Farm is essential for ensuring that your applications and websites perform at their best and are always accessible. This guide will walk you through the process of updating your GSLB Farm.
Once you have created a GSLB Farm, you need to add the following configurations to the appropriate sections:
- Global
- Services
- Zones
- IPDS
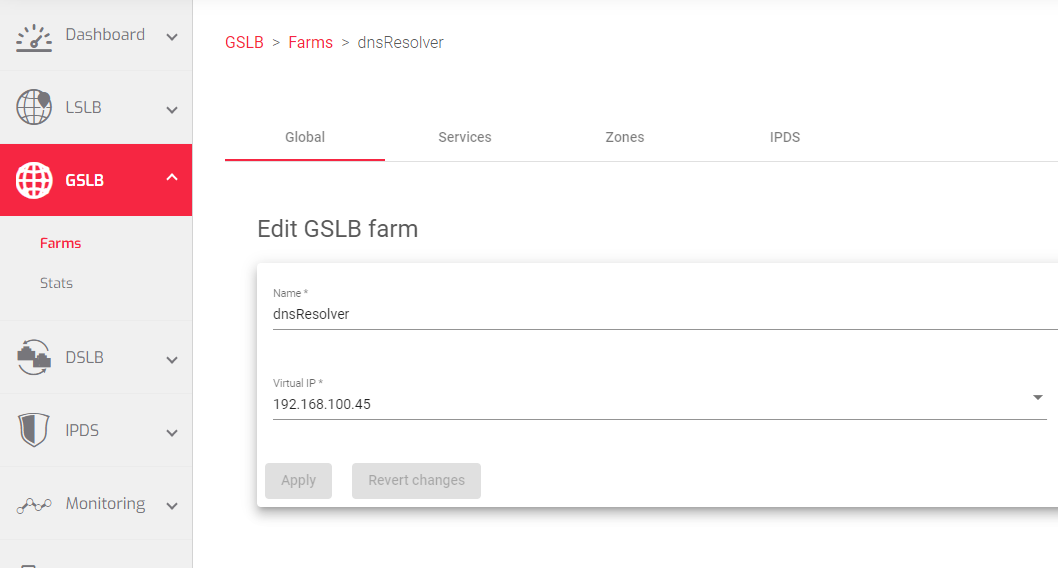
Global
The fields to update within the global section include:
- Name: A name that uniquely identifies the GSLB farm.
- Virtual IP: An IP address that the farm will listen to for incoming DNS queries.
- Virtual Port: The Port on which the ADC will listen for incoming DNS queries.
Services
The Services section of the GSLB Farm configuration allows you to define load balancing rules, optimizing the performance and availability of your applications. SKUDONET offers two primary traffic distribution methods: Priority, which prioritizes traffic based on a predetermined order, and Round Robin, which distributes traffic evenly across available data centers.
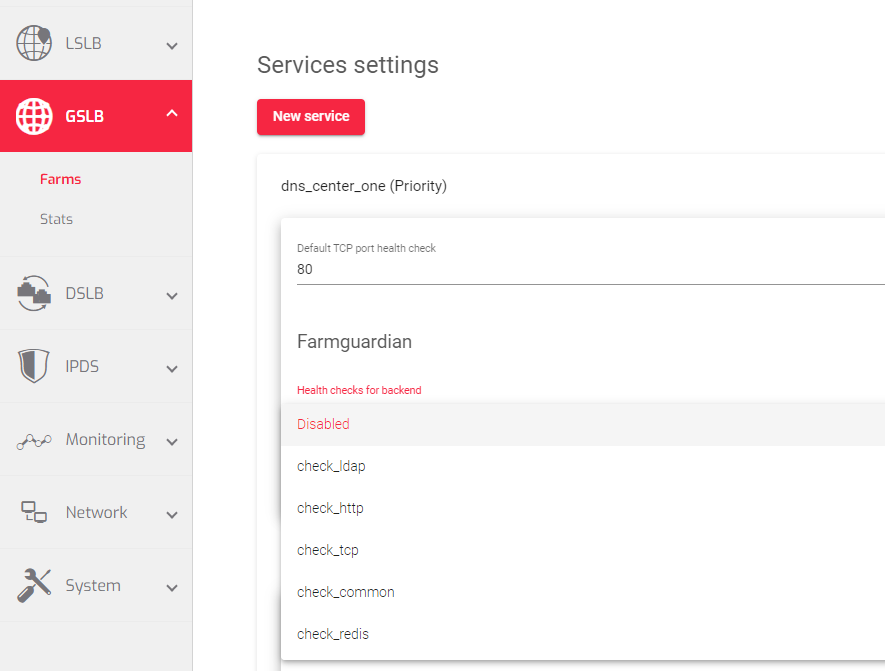
In addition to load balancing rules, the Services section enables you to add Backend servers pointing to specific data centers. Farmguardian, a dedicated daemon, continuously monitors the health of these backend servers, ensuring that only healthy servers receive traffic. This proactive monitoring ensures that your applications remain highly available and performant.
Default TCP port health check: Checks the availability of a backend server by attempting to establish a TCP connection to the server’s port 80.
Farmguardian
Like the L4xNAT profile, GSLB farms lack built-in health checks for backends, making it necessary to configure Farmguardian for this virtual service.
You can assign either the default or personalized advanced health checks to this service from any existing farmguardian check.
For further information about Farmguardian, go to the Monitoring >> Farmguardian section.
After selecting the Farmguardian rule, it will be automatically applied to the farm.
Backends
The backends section is where you add the IP addresses of the backend servers. This is where you specify the servers that will receive traffic from the GSLB Farm.
To add a backend server:
- Hover over the preconfigured backend and click the Edit Icon.
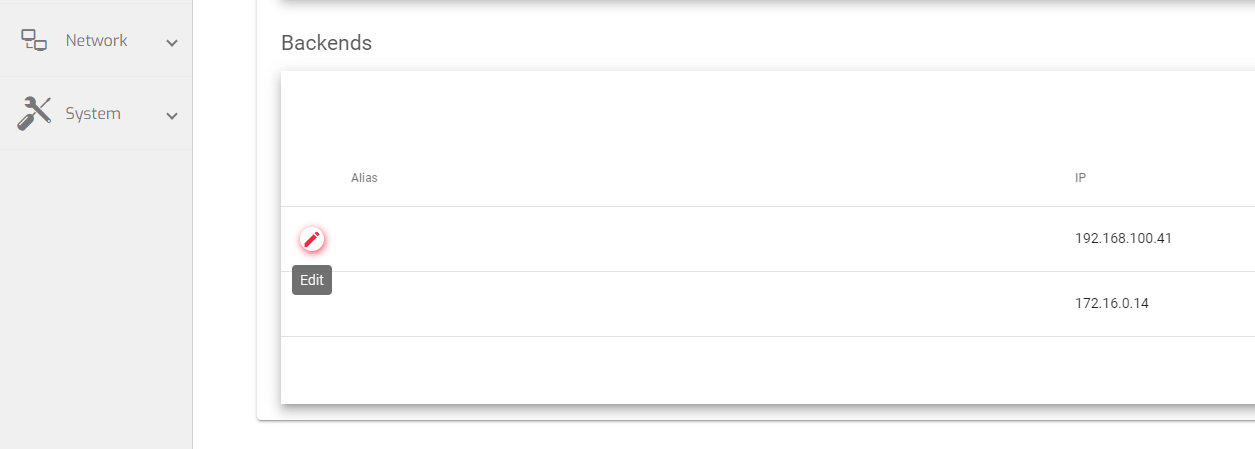
- In the Alias field, Choose to add a Custom IP or a preconfigured one with an Alias.
- If you chose the Custom IP field, add the Ip address of that backend server.
- Click the Apply button.
The image below shows a table containing the backend servers that the GSLB farm will forward the traffic to.
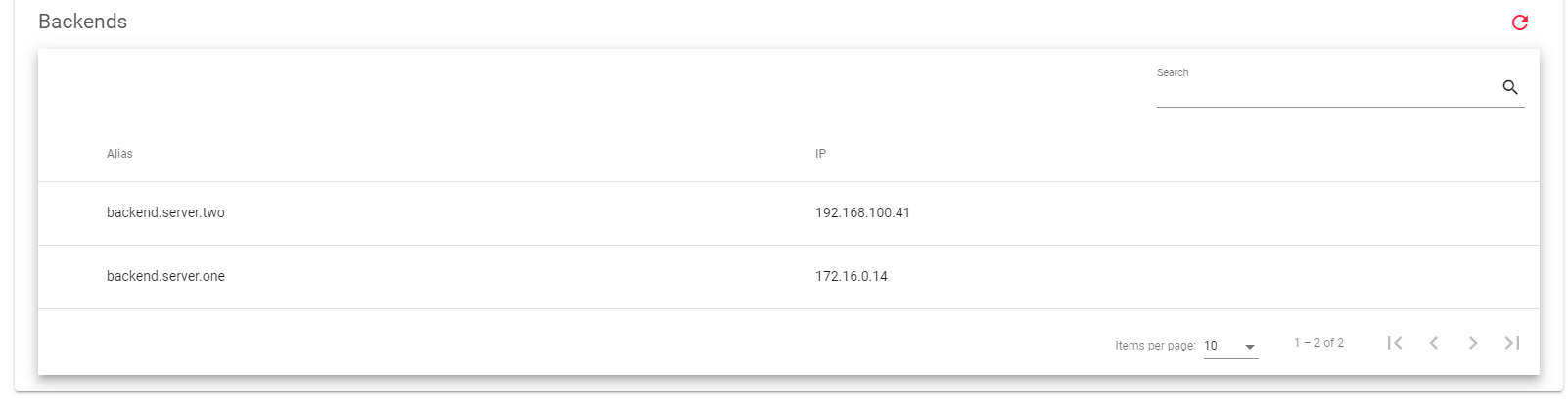
Here is a brief description of each field in the above table.
- Alias: A name that easily Identifies the backend server.
- IP: The IP address of the backend serve that will listen for incoming trafic from the GSLB farm.
Zones
Once you’ve established your GSLB Farm, the Zones section plays a crucial role in optimizing its performance by managing and updating DNS records. These records map domain names to IP addresses, ensuring that users are directed to the most appropriate servers for their location and network conditions.
The Zones section provides a comprehensive interface for managing DNS records, allowing you to add, edit, and delete records as needed. You can specify the record type, set the record value, and configure additional parameters to ensure that your DNS records accurately reflect your GSLB Farm configuration.
Default name server This is the DNS server that is automatically assigned to a domain name when it is registered.
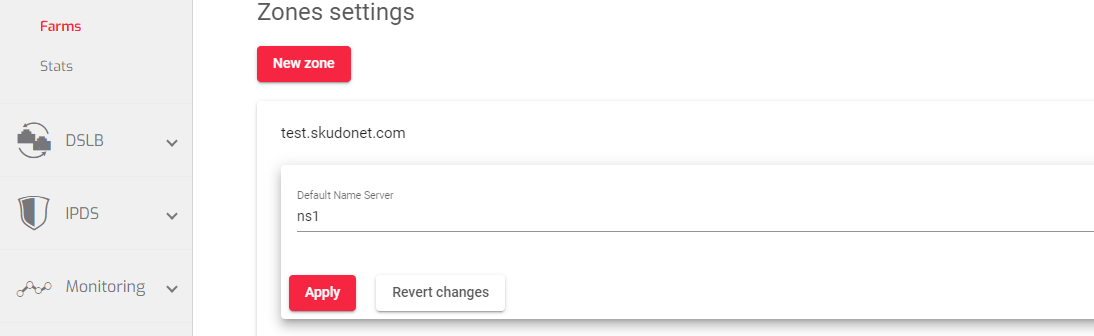
Resources
This section contains all the DNS records one may configure within the GSLB Farm. Here is a brief description of each DNS record:
- A: An A record maps a domain name to an IPv4 address.
- NS: An NS record specifies the name servers for a domain.
- AAAA: An AAAA record maps a domain name to an IPv6 address.
- CNAME: A CNAME record is an alias for another domain name.
- MX: An MX record specifies the mail servers for a domain.
- SRV: An SRV record specifies the location of services for a domain, such as web servers or mail servers.
- TXT: A TXT record is used to store arbitrary text information about a domain.
- PTR: A PTR record is used to map an IP address to a domain name.
- NAPTR: A NAPTR record is used to specify the location of services for a domain, such as web servers or mail servers, in the presence of multiple protocols.
- Services: A Services record is used to specify the location of services for a domain, such as web servers or mail servers, using DNS-SD.
The image below shows the resources added to the configured GSLB Farm.

Here is a brief description of each field in the image above:
- Name: The domain name or hostname associated with the DNS record.
- TTL: The time in seconds that a DNS record should be cached by DNS resolvers.
- Type: The type of DNS record, indicating the information it provides.
- Data: The specific information associated with the DNS record, depending on the record type.
IPDS Rules for GSLB farms
This section allows you to enable IPDS rules. IPDS stands for Intrusion Prevention and Detection System. It is a security system that protects your network from attacks.
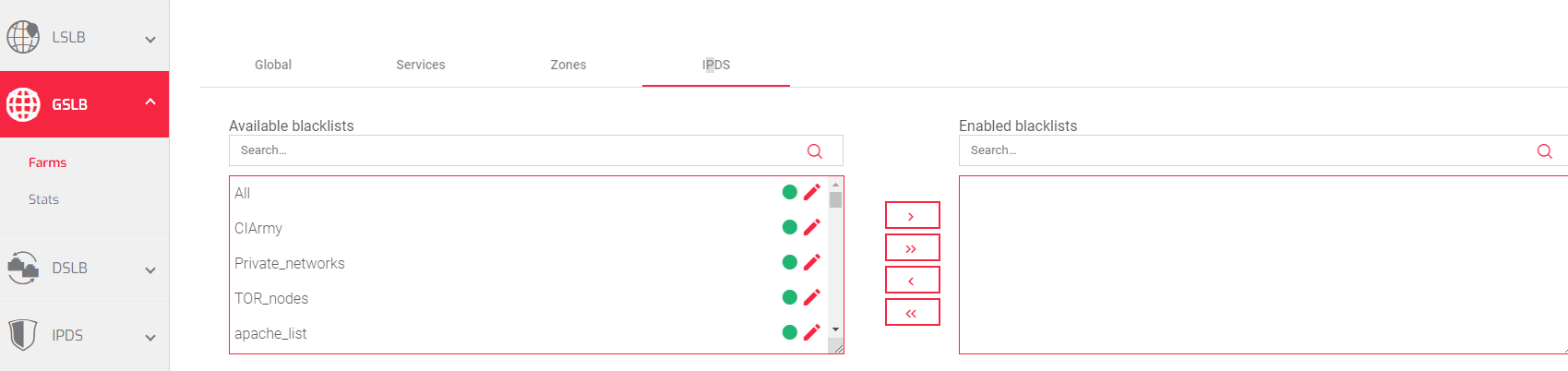
There are four types of IPDS rules:
- Blacklist: Rules that block traffic from known malicious IP addresses.
- DoS: Rules that protect against denial-of-service attacks.
- WAF: Rules that protect against web application attacks.
- RBL: Rules that block traffic from known malicious domains.
For each type of IPDS rule, there are two tables:
Available: This table shows all of the IPDS rules of that type that are available to you.
Enabled: This table shows all of the IPDS rules of that type that are currently enabled for the selected farm.
To add an IPDS rule to a farm:
- Select the desired rule from the Available table.
- Click the forward arrow.
To delete an IPDS rule from a farm:
- Select the desired rule from the Enabled table.
- Click the back than arrow.
You can also add or remove all of the IPDS rules of a certain type at once by clicking the right or left double arrows.
To edit an IPDS rule:
- Click the Edit icon next to the rule.
You cannot create new IPDS rules from the farm view. To create a new IPDS rule, you must go to the IPDS section.
Next Article: LSLB | Stats