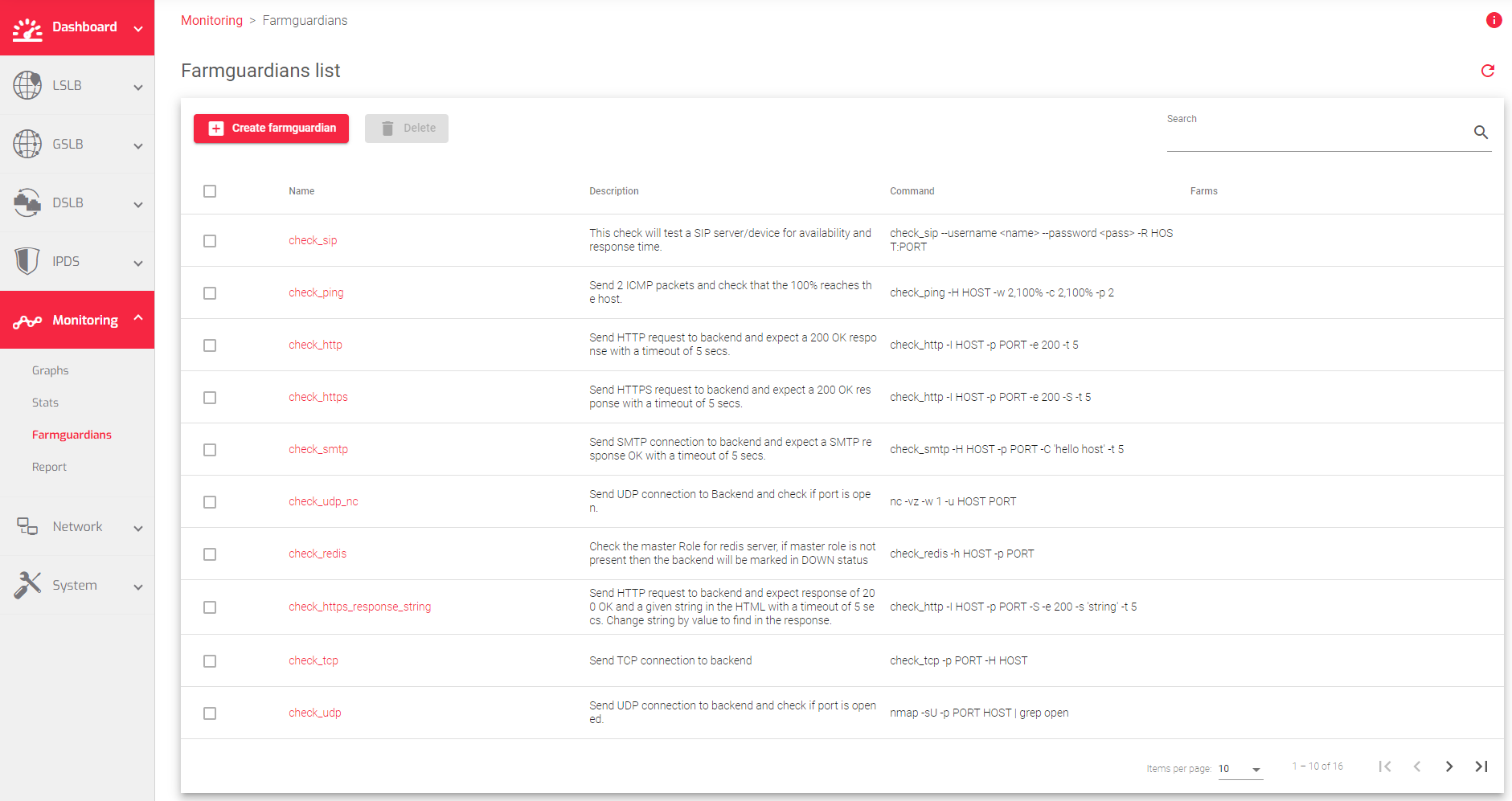
The Farmguardian section lists all the health checks available in the load balancer. It also includes a brief description of each check and the farms where they are applied.
Farmguardian is used for advanced monitoring of the backends. When Farmguardian detects a problem, it automatically disconnects from the real server and marks its IP address as blacklisted.
Health checks can be either pre-configured or custom. The two types of checks can be identified by the action column. Each check with a grayed-out configuration setting is pre-configured, and those that are editable after clicking the pencil icon are custom.
The image below shows a list of Farmguardian rules:
Actions: To manage Farmguardian checks, you can use the following actions from the Action menu:
- Create Farmguardian: Opens the farmguardian form where you can fill in the necessary information to create a new check.
- Delete: Removes the selected farmguardian check.
The Farmguardian table contains the following information:
Name: A descriptive name of the Farmguardian check.
Description: A description of the Farmguardian check.
Command: The command and parameters to be executed on every interval against each backend of the farm.
Farms: The farms and services that use the Farmguardian check.
Actions: The following actions can be used to manage the Farmguardian check:
- Edit: Opens the configuration screen for the Farmguardian check. This action is only available for custom farmguardian checks.
- Delete: Deletes the selected Farmguardian check. If the check is assigned to any service, a notification will ask you if you want to force the deletion. This action is only available for custom farmguardian checks.
Preconfigured Health-Checks
These are the built-in health checks for your farms.
| health checks | Description |
|---|---|
| check_redis | Checks if a Redis server is running in master role. If it is not, the backend is marked as down. |
| check_tcp | Sends a TCP connection to the backend and checks if it is successful. |
| check_udp | Sends a UDP connection to the backend and checks if the port is open. |
| check_http | Sends an HTTP request to the backend and expects a 200 OK response within 5 seconds. |
| check_https | Sends an HTTPS request to the backend and expects a 200 OK response within 5 seconds. |
| check_smtp | Sends an SMTP connection to the backend and expects an SMTP OK response within 5 seconds. |
| check_http_response_string | Sends an HTTP request to the backend and expects a 200 OK response and a given string in the HTML within 5 seconds. The string can be changed to any value that you want to find in the response. |
| check_https_response_string | Sends an HTTPS request to the backend and expects a 200 OK response and a given string in the HTML within 5 seconds. The string can be changed to any value that you want to find in the response. |
| check_pop | Sends a POP connection to the backend and expects a POP OK response within 5 seconds. |
| check_ldap | Sends an LDAP query to the backend and expects an LDAP bind within 5 seconds. The base search, user to bind, and user password can be changed. |
| check_ldaps | Sends an LDAPS query to the backend and expects an LDAP bind within 5 seconds. The base search, user to bind, and user password can be changed. |
| check_imap | Sends an IMAP connection to the backend and expects an IMAP OK response within 5 seconds. |
| check_top | Sends a TCP connection to the backend. |
| check_sip | Tests a SIP server/device for availability and response time. |
| check_ping | Sends 2 ICMP packets and checks if they both reach the host. |
| check_common | Checks the folder /usr/lib/nagios/plugins, which includes more checks. More information about each health check can be obtained by running the check with the –help option. |
Next Article: Monitoring | Farmguardians | Create