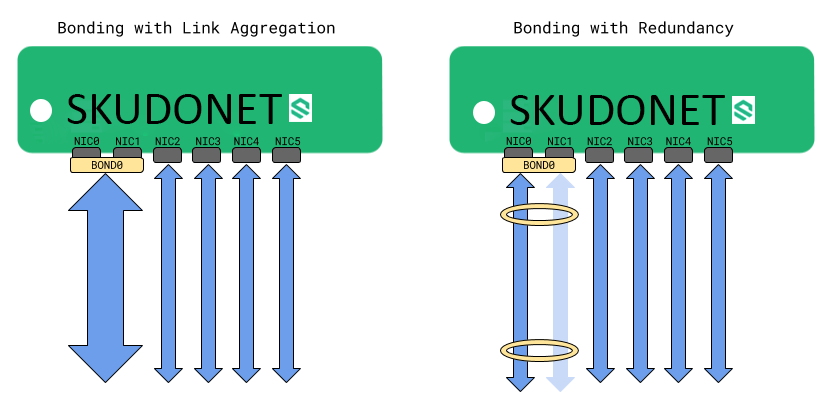
Network bonding (also known as link aggregation, NIC teaming) combines multiple physical network interfaces into a single logical interface. This enhances network performance by distributing traffic across multiple NICs, improving load balancing and throughput. Additionally, network bonding provides redundancy by enabling failover between NICs in case of failure.
The image below demonstrates how SKUDONET performs network bonding with Link Aggregation and With Redundancy
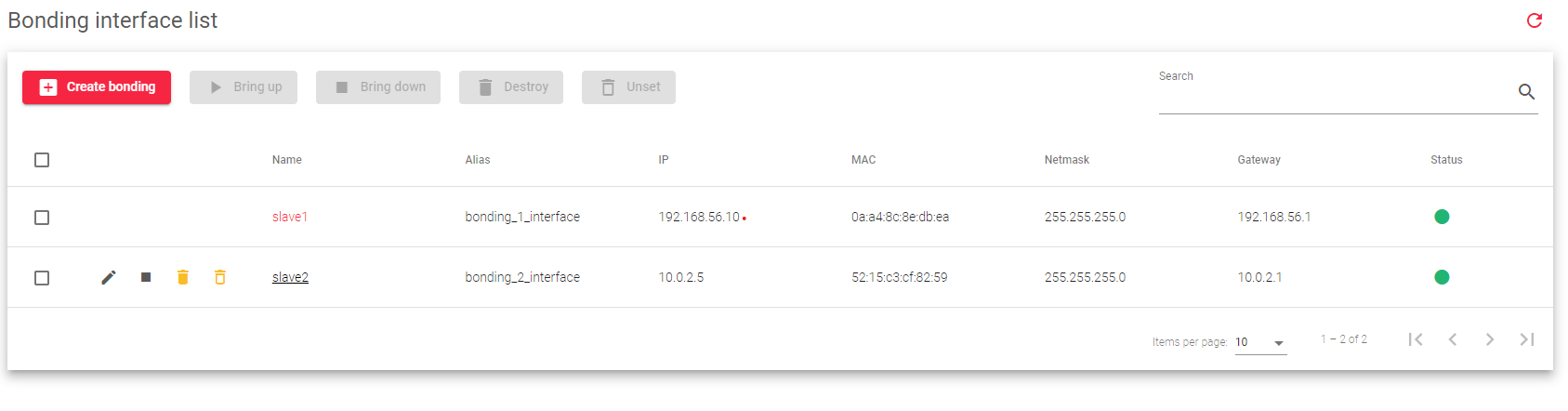
Network Bonding Interfaces List
The image below lists all of the network bonding interfaces that are configured on the system.
The table includes the following columns:
Name: The unique identifier for the bonding interface.
Alias: An alternative name for the bonding interface.
IP: The Internet Protocol (IP) address assigned to the bonding interface, enabling it to communicate on the network. Supports both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
MAC: The Media Access Control (MAC) address, a unique identifier for the bonding interface on the network hardware level.
Netmask: The subnet mask defines the network segment to which the bonding interface belongs.
Gateway: The default gateway acts as a routing destination for traffic originating from the bonding interface.
Status: Displays the availability of the bonding interface by use of the color indicators:
- Green: Indicates that the bonding interface is UP.
- Red: Indicates that the bonding interface is DOWN.
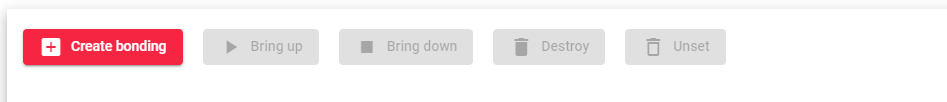
Actions: The available actions for each bonding interface in the table:
- Create bonding: This option redirects you to the bonding interface creation form.
- Bring up: Start the selected interfaces and configure them to accept traffic.
- Bring down: Shut down the selected interfaces and stop them from accepting traffic.
- Destroy: Remove the bonding interface, but only if the configuration is empty. The bonding interface will disappear and the slave interfaces will be available again.
- Unset: Remove the selected interface configurations.
Next Article: Network | Bonding | Create