A floating IP, also known as a virtual IP (VIP), is a dynamic IP address that can be assigned to different physical servers in a network. This allows network traffic to be seamlessly redirected to the remaining active servers in the event of a failure, ensuring continuous service availability.
Floating IPs are often used in conjunction with a protocol called Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP). VRRP is a standard protocol that dynamically selects a primary server to advertise the floating IP to the network. When the primary server fails, VRRP automatically selects a new primary server and assigns the floating IP to it. This ensures that traffic continues to flow to the correct server even if the primary server fails.
Floating IPs Table
This table lists all of the floating IPs configured in the system, as well as any interface with a configuration set where a floating IP can be configured.
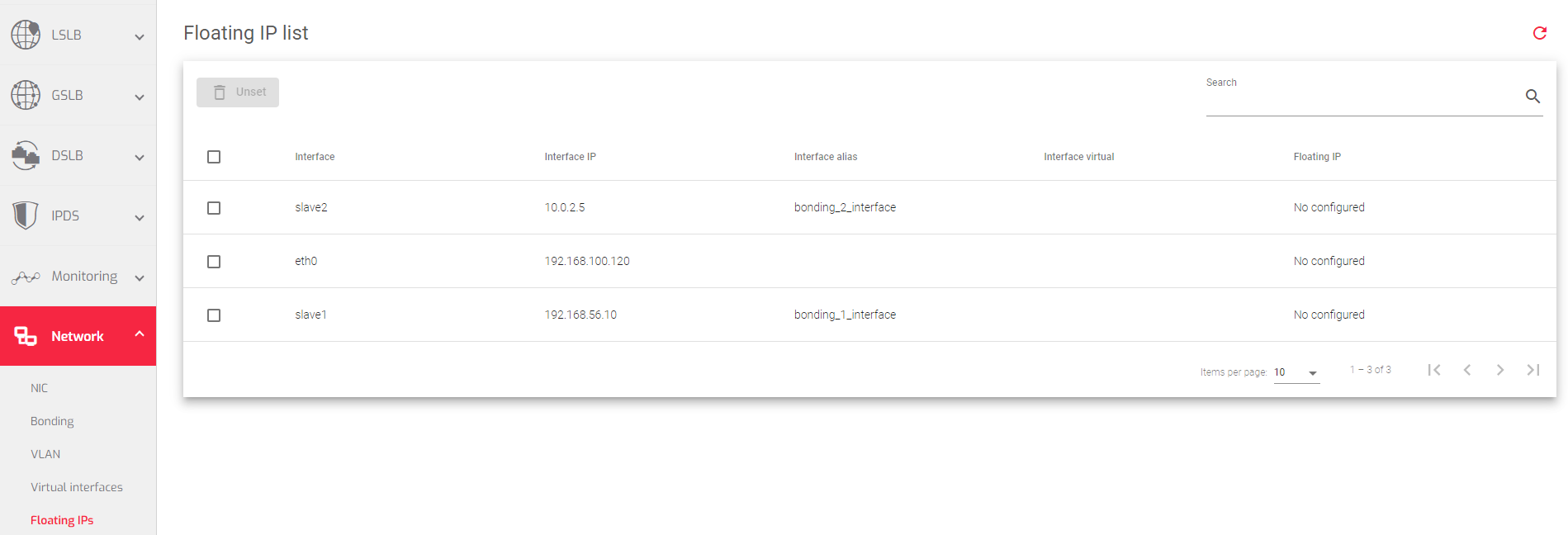
The table above includes the following fields:
Interface: The name of the physical or virtual interface to which the floating IP address will be assigned. This can be a VLAN, bonding, or NIC interface.
Interface IP: The IP address of the parent interface.
Interface alias: A nick name or a different name that easily identifies the interface from the rest.
Interface Virtual: The name of the virtual interface from which the floating IP address will be inherited.
Floating IP: The IP address that will be assigned to the parent interface. This IP address must be inherited from a virtual interface.
Actions: The actions that can be performed on the floating IP address:
- Configure: Assigns the floating IP address to the parent interface. Only one floating IP address can be assigned to a parent interface.
- Unset: Clears the configuration and removes the floating IP address from the parent interface.
Next Article: Network | Floating IPs | Configure