Contents
What is ADFS and how does it work?
Active Directory Federation Services, commonly known as ADFS, is a solution from Microsoft to provide Single sign-on and web-based authentication to systems and applications between organizations with unique or multiple domains.
ADFS uses the claims-based access control authorization model to ensure the application level security and federation identity, which is implemented between two organizations by establishing trust between two security zones or scopes.
Two federation servers are required, one for user accounting and authentication (mainly with Active Directory Domain Services) to identify them and another for resource authorization and user access validation. This architecture allows a user that belongs to another security scope or realm to control their access directly without sharing databases or passwords between them.
ADFS is designed to communicate over HTTPS to validate the user with a given username and password, then, if this is valid the service returns a unique token that can be used by third-party applications.
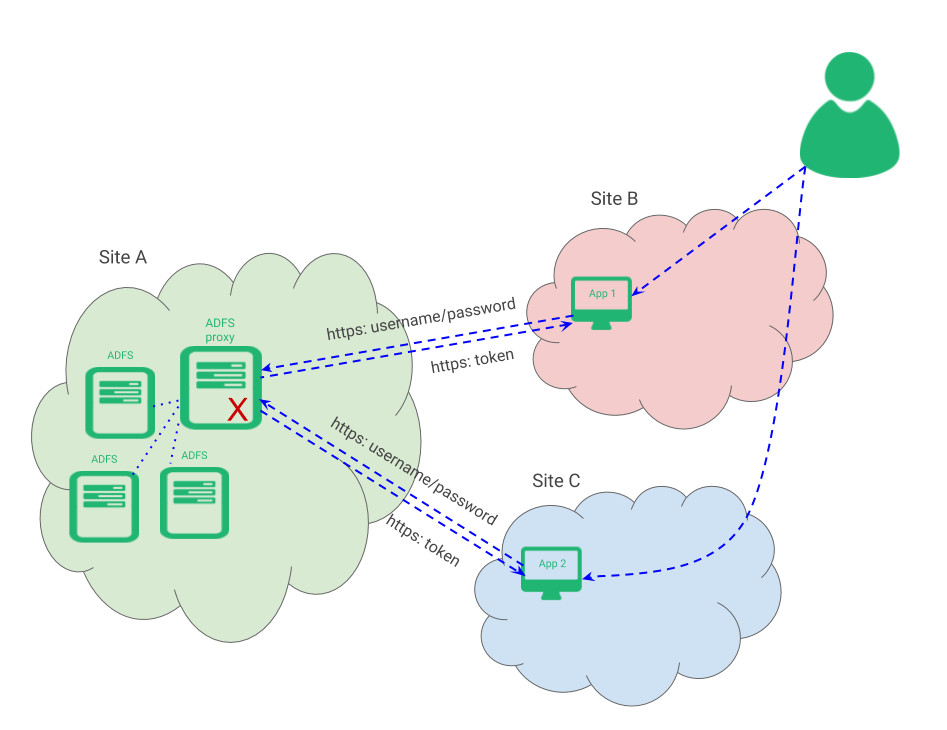
When a certain user attempts to access an application on one site, it redirects the login petition from the user to the main site ADFS proxy in the form of username and password and then returns a token that will be used by the application to control the user accesses.
The problem of that environment is the single point of failure and the lack of scalability once the organization grows.
ADFS scalable environment
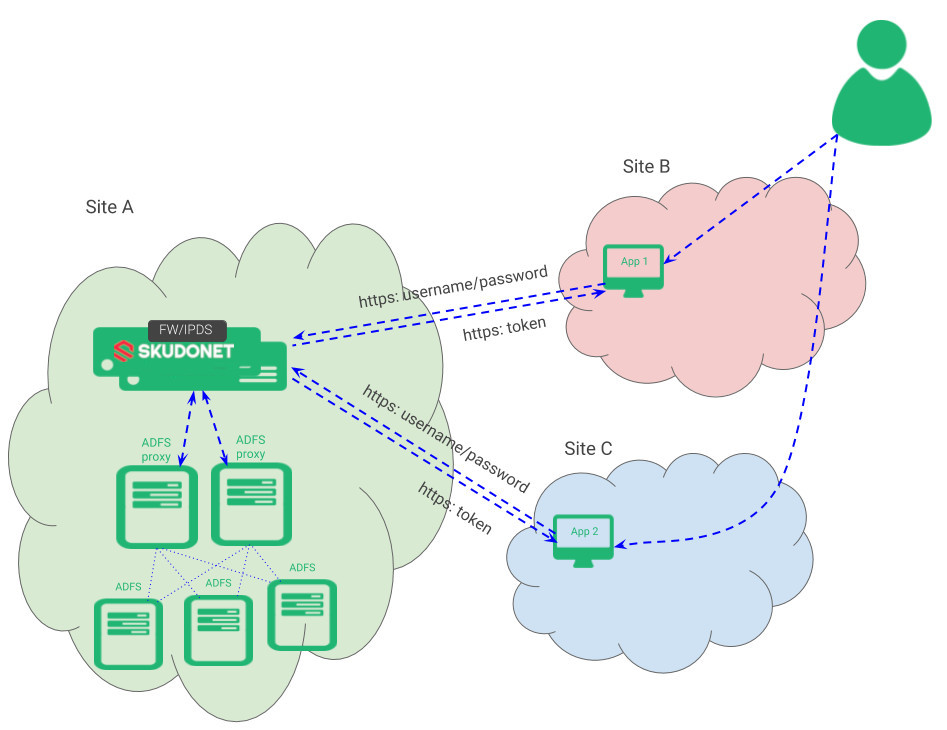
To provide high availability, load balancing and automatic disaster recovery of ADFS services, we’re proposing an environment like it’s shown below.
This approach is implementing load balancing and high availability for in-site services, but it can be built as an inter-site architecture which also provides automated disaster recovery for geo-located ADFS services.
ADFS load balancing configuration
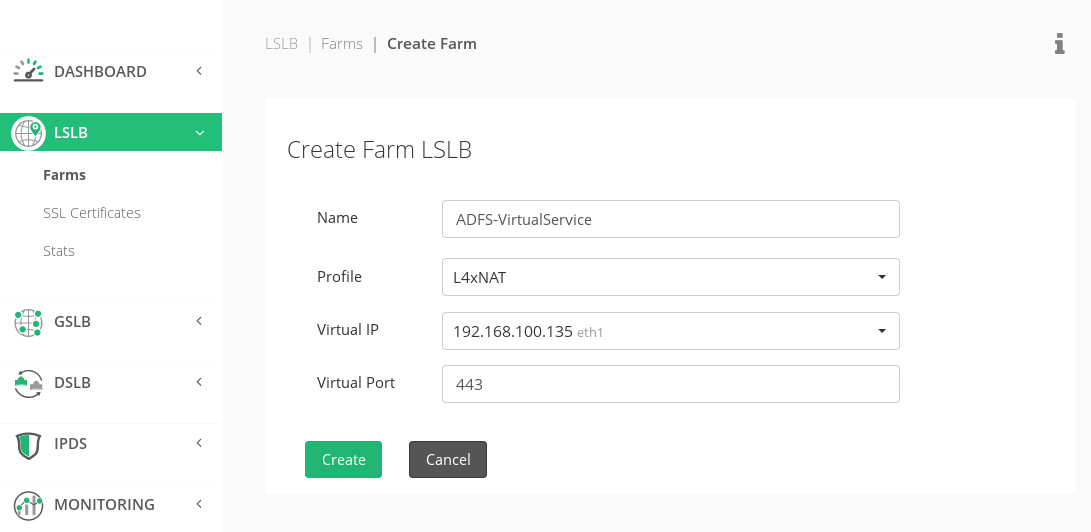
Creating a simple load-balancing virtual service with LSLB | L4xNAT farm will allow to load balance of the HTTPS requests as raw TCP connections.
In the Services tab, select the dispatcher algorithm selected and configure the ADFS proxies in the backends section.
Finally, configure the advanced health checks for ADFSv2:
./check_http --sni -H fs.mydomain.com -IHOST -u /adfs/ls/idpinitiatedsignon.aspx -e 200 -S -s html
for ADFSv3:
./check_http --sni -H fs.mydomain.com -IHOST -u /adfs/ls/idpinitiatedsignon.htm -e 200 -S -s html
Note: In the health checks commands, change your ADFS domain.
ADFS in high availability and automated disaster recovery configuration
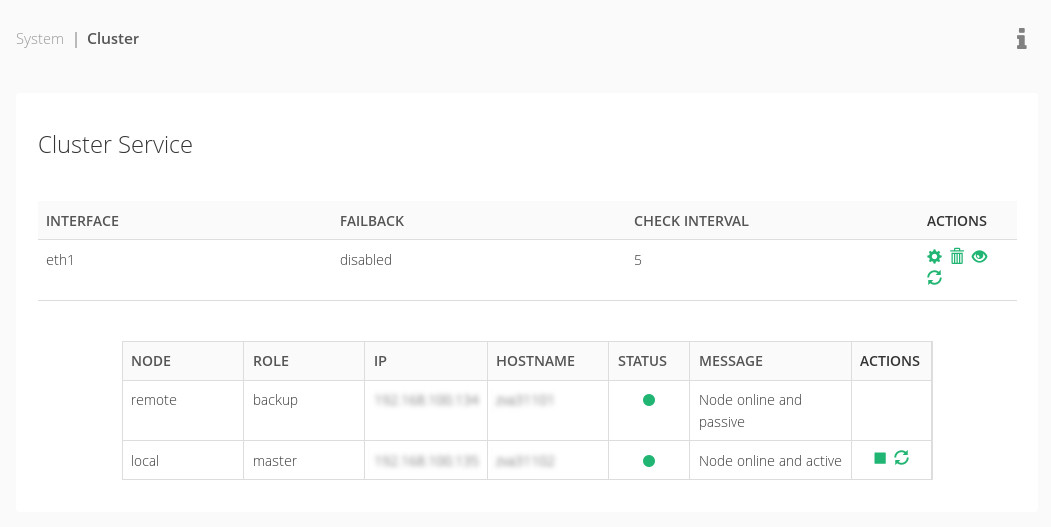
As the SKUDONET clustering solution replicates all the connections and sessions in real-time, building a cluster the clients can transparently be switched from one node to another without disruption. The cluster service provides high availability at the application delivery layer but also automatic disaster recovery abilities that can be configured easily through the section System | Cluster.
ADFS enhanced security
SKUDONET Intrusion Prevention and Detection System adds a security layer to the ADFS services, so we can ensure that the connection requests from our sites are trusted.
In addition, SSL offload for ADFS will be available soon so the complete security layer could be delivered by SKUDONET by loading the SSL certificate in an LSLB | HTTP farm with an HTTPS listener.