Overview
Diffie-Hellman key exchange (D-H) is a method to generate a private key between two machines connected through an insecure channel.
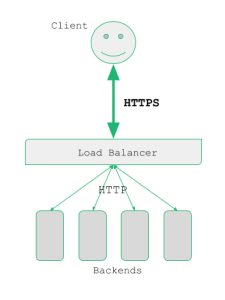
When a client begins a connection to a secured web service the SSL negotiation occurs by exchanging the public keys and then, the two parties come into an agreement in regards to the keys and ciphers to be used during the communication.
In this illustration is perfectly explained how the negotiation behaves with colors. Just imagine how it works with large random numbers computed by both communication nodes.
How it’s used in a load balancer
The load balancer creates SSL services when it performs SSL Offload operations, in the form:
SKUDONET Open source Load Balancer uses the OpenSSL tools with dhparam options to generate the Diffie-Hellman keys. Read more about the full options here.
To create a SSL Offload farm (HTTP profile with HTTPS listener in SKUDONET Open SOurce Load Balancer) it’s required to generate a Diffie-Hellman key with the following good practices to ensure a robust key generation.
1. A minimum key length of 2048 bits. More length will mean more difficult to decrypt in a reasonable amount of time.
2. One DH key per SSL farm to make it more difficult to break the communication of several SSL services and isolate the security of every farm.
3. Less predictable in the random generation means more difficult to break communication.
Note that the generation of the Diffie-Hellman keys is usually a computationally costly process due to the random number generation could take too much time, but this ensures a security assurance for our SSL services.
All this procedure is done automatically by the SKUDONET library, it doesn’t require any action by the system administration, the aim of this document is only to inform about the process.
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diffie-Hellman_key_exchange
http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Diffie-HellmanProtocol.html